Periodontology
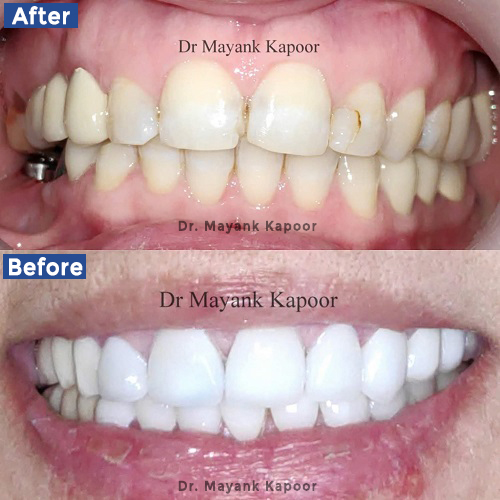
Periodontology, also known as periodontics, is a specialized branch of dentistry that focuses on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases that affect the supporting structures of the teeth, such as the gums, periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone.
Scaling & Polishing
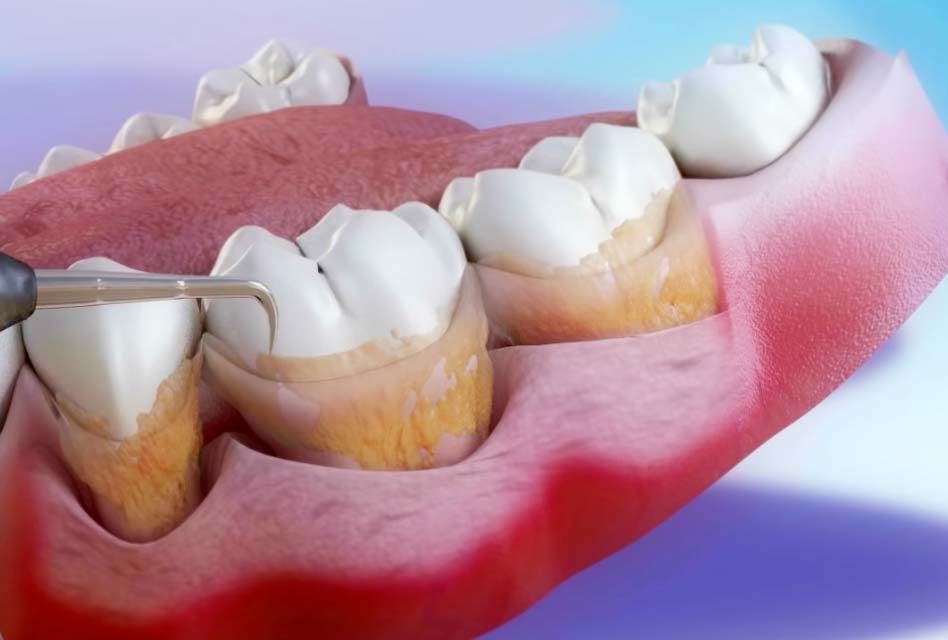
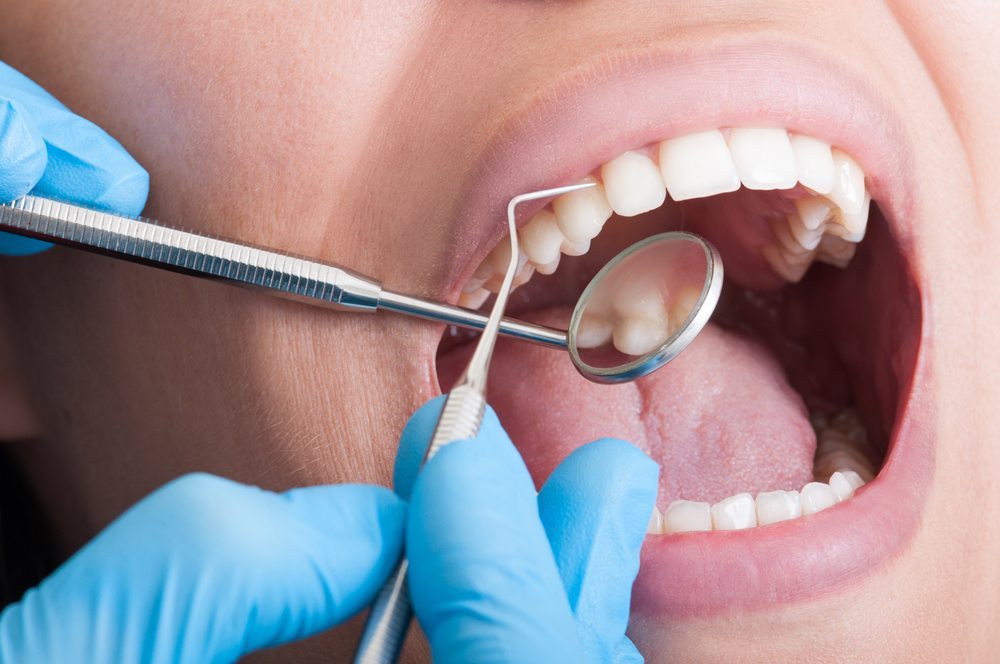
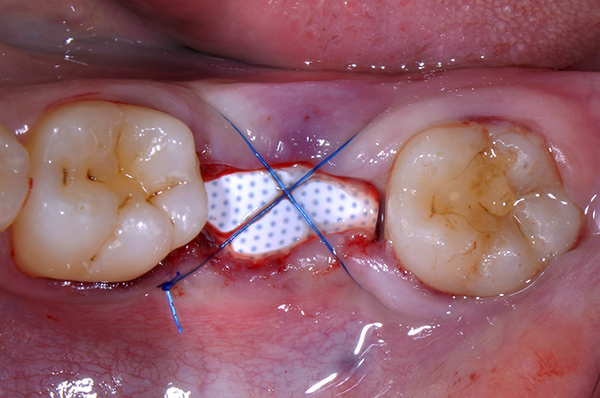
Scaling is a non-surgical procedure that involves the thorough removal of plaque, tartar (calculus), and other deposits that accumulate on the surfaces of the teeth and below the gum line. These deposits contain harmful bacteria that can lead to gum inflammation and periodontal disease.
After scaling and root planing, the teeth are polished. Polishing involves using a specialized dental instrument or a polishing paste to remove stains and residual plaque or tartar that may remain on the tooth surfaces. Polishing creates a smooth and shiny surface, which makes it more difficult for plaque to adhere to the teeth.
Curettage
A periodontal procedure called curettage, involves removing the unhealthy or infected soft tissue that lines the periodontal pockets. It is frequently carried out as a component of periodontal disease treatment.
The primary goal of curettage is to eliminate inflamed or infected tissue within the periodontal pockets. Periodontal pockets are the spaces that form between the gums and teeth when gum disease progresses. These pockets harbor harmful bacteria and toxins that contribute to the progression of periodontal disease. By removing the diseased tissue, curettage aims to promote the healing and regeneration of the gum tissue.
Flap Surgery & Root Planning
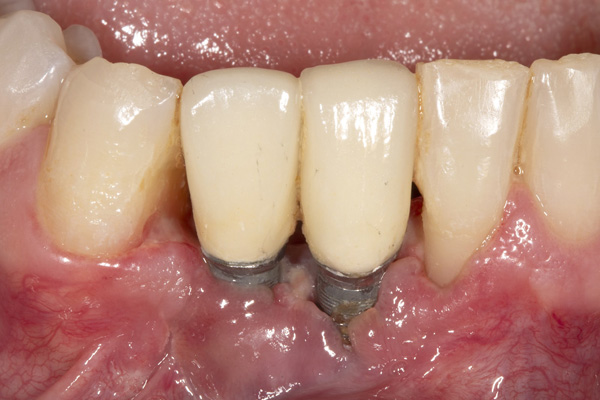
Flap surgery, also known as periodontal flap surgery or pocket reduction surgery, is a periodontal procedure that is performed to treat advanced periodontal disease. It is typically done in conjunction with root planing.
The primary goal of flap surgery is to access and clean the deep pockets that have formed between the gums and teeth due to advanced periodontal disease. These pockets are difficult to clean with regular oral hygiene practices and require surgical intervention to thoroughly remove plaque, tartar, and diseased tissue.
Root planing is often performed during flap surgery to smoothen the tooth roots, removing rough areas that can harbor bacteria and contribute to the disease.
Guided Bone Regeneration
Guided bone regeneration (GBR) is a surgical technique used in dentistry and periodontology to regenerate bone in areas where it has been lost or damaged due to periodontal disease, trauma, or tooth extraction. The procedure involves the use of barrier membranes and bone graft materials to promote the growth of new bone in the desired area.
Different types of barrier membranes and bone graft materials can be used in guided bone regeneration. Barrier membranes can be made of synthetic materials or derived from animal sources.
Following guided bone regeneration, the body’s natural healing process takes place. The barrier membrane helps to maintain space for new bone growth and prevents soft tissue ingrowth, while the bone graft material serves as a scaffold for new bone formation. Over time, the graft material is resorbed and replaced by the patient’s own bone.
Soft Tissue Graft & PRF Membrane Guided Treatment
A soft tissue graft, also known as a gum graft or gingival graft, is a surgical procedure performed in dentistry to restore or enhance the gum tissue in areas where it has receded or been lost. The procedure involves taking tissue from one area of the mouth (donor site) and transplanting it to the area in need of additional gum tissue (recipient site). Soft tissue grafts are commonly performed to address issues such as gum recession, root exposure, and to improve the esthetics and health of the gum line.
Gum recession can occur due to various factors, including periodontal disease, aggressive tooth brushing, genetic predisposition, trauma, or tooth misalignment. Gum recession can lead to tooth sensitivity, root exposure, increased risk of decay, and compromised esthetics. Soft tissue grafting helps to cover exposed tooth roots, increase gum thickness, improve gumline appearance, and protect the underlying tooth structure.
PRF (Platelet-Rich Fibrin) membrane-guided treatment is a regenerative procedure used in dentistry and oral surgery to enhance healing and tissue regeneration. PRF is derived from a patient’s own blood and contains concentrated platelets, growth factors, and other bioactive substances that promote tissue healing and regeneration. The PRF membrane is a key component of this treatment.
To create the PRF membrane, a small amount of the patient’s blood is drawn and placed in a centrifuge machine. The centrifuge spins the blood at a specific speed, separating it into various layers. The PRF layer, consisting of fibrin and platelets, is isolated and used to form the membrane.
Laser Gingivectomy & Gingivoplasty
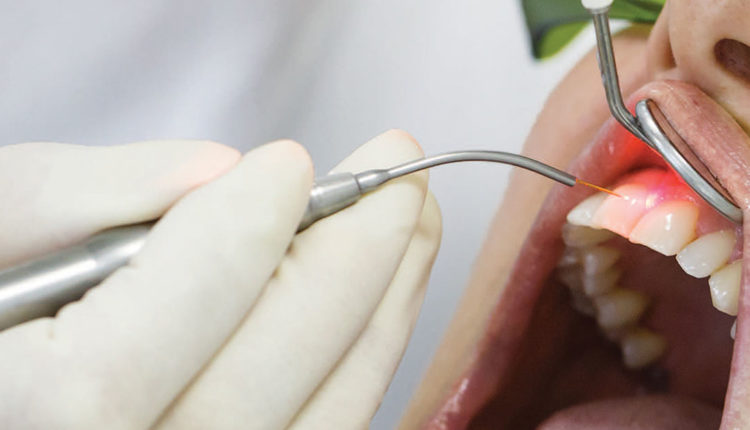
Laser gingivectomy is a dental procedure that uses laser technology to remove or reshape gum tissue. It is often performed to treat conditions such as excessive gum tissue (gummy smile), periodontal disease, or to create a more esthetic gum line.
Laser gingivectomy involves the use of a dental laser, typically a diode laser or an erbium laser. The laser emits a highly focused beam of light energy that selectively removes or vaporizes the gum tissue. The laser can precisely target the specific area, allowing for controlled and accurate removal of excess or diseased gum tissue. The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia to ensure patient comfort.
patients are usually provided with post-operative care instructions. These may include guidelines for oral hygiene, such as gentle brushing and rinsing with an antimicrobial mouthwash. Pain medication or antibiotics may be prescribed if needed. Follow-up visits will be scheduled to monitor healing and ensure proper recovery.